In order to work with databases, EF Core follows 2 types of approach:
- Code First
- Database First
Database First is the traditional approach wherein we will first create the required database and dependencies, then consume it on the application. We will study the same with example in our next article.
In Code First approach, the database is created by the model class. In simple words, the programmer will create a class with required properties, set the Key and other attributes using Data Annotation and hook it up with the model inherited from EF Core’s DB context and ensure the database being created from the defined layout.
Lets understand this with an example. I want to create a SQL table ‘MyBookTable’ through Code First Model, so instead of going to SQL and executing queries I will first write the code.
Book.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Internal;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyBookStoreEF.Models
{
public class Book
{
public int BookID { get; set; }
public string BookName { get; set; }
public string BookAuthor { get; set; }
public Book()
{
BookStoreModel bookModel = new BookStoreModel();
bookModel.Database.EnsureCreated();
}
}
}
BookStoreModel.cs
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Metadata.Internal;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyBookStoreEF.Models
{
public class BookStoreModel : DbContext
{
public string connString = @"Data Source=DESKTOP-TAE8O0I\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=BooksDB;Integrated Security=True;Pooling=False";
public DbSet<Book> Book { get; set; }
public BookStoreModel()
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(connString);
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Book>().ToTable("MyBookTable");
}
}
}
In our above code, we created a simple Book class with basic properties. Created a BookStoreModel.cs from DbContext and instructed to use the sqlserver in the OnConfiguring() method. The Book class is mapped to ‘MyBookTable’ sql table in the OnModelCreating() method which is used to create the model and mappings in the memory.
In the constructor Book(), when we create an instance of BookStoreModel, the framework loads the required model in the memory and the Database.EnsureCreated() will ensure the actual schema being translated to the connected database.
Let’s create a sample MVC Core controller to see the full example:
HomeController.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using MyBookStoreEF.Models;
namespace MyBookStoreEF.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
public IActionResult Index()
{
Book book = new Book();
book.BookName = "Learn EF Core";
book.BookAuthor = "Naved";
BookStoreModel model = new BookStoreModel();
model.Book.Add(book);
model.SaveChanges();
return View();
}
public IActionResult Privacy()
{
return View();
}
[ResponseCache(Duration = 0, Location = ResponseCacheLocation.None, NoStore = true)]
public IActionResult Error()
{
return View(new ErrorViewModel { RequestId = Activity.Current?.Id ?? HttpContext.TraceIdentifier });
}
}
}
The above is a simple controller class with default action Index() where we are creating a simple object of Book Class and adding BookName and BookAuthor. As soon as the code in Index method is executed, check the database, you will find a new table ‘MyBookTable’ as defined by the model and a first record with BookName and BookAuthor has been inserted.
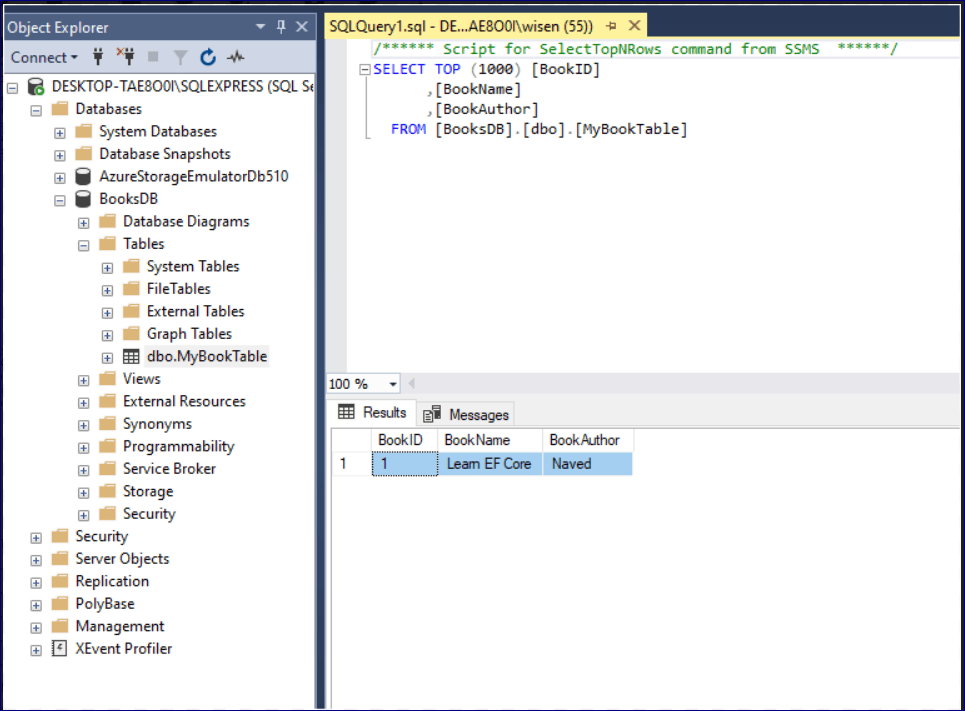
In this way you can control database creation using the model code. In the next article we will go through Database First approach.