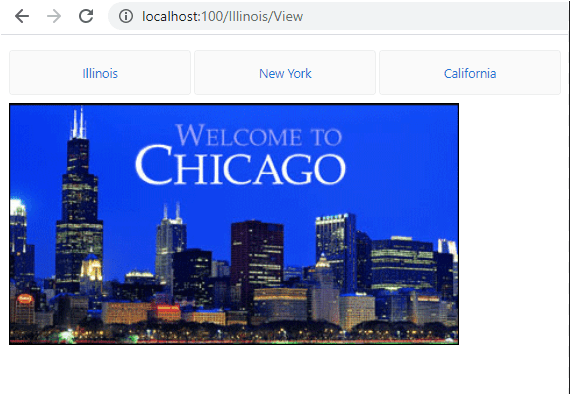
Lazy Loading
In the previous example with Routing, there was problem wherein all the 3 components (IllinoisComponent, NewYorkComponent, CaliforniaComponent) were loaded together on page load. This can be seen on Chrome >> Developer Tools >> Network tab under Main.js file.
Now the problem is when there are a lot of components used in the routing collection, loading all of them at once on page load will not only cause to increase the use of browser resources but also impacts the performance of the application significantly.
Angular has provided a solution to this problem by implementing a feature called as Lazy Loading. It means ‘Load components only when they are called’, this is achieved by implementing a concept wherein the subsequent routes are defined as child routes and called only when the request for that routes comes in the browser.
The following example will clear this concept. Please see the project structure below. The difference in the previous is that we are creating separate modules and route files for each component. The interlinking between these modules and route files will be triggered only then they are called thus we define them as child routes.
The main route file ‘Routing.ts’ would define the Illinois/NewYork/California components as Child routes and it dictates the browser to only load them though loadchildren() method only when they are requested. The default route will be app component which is used to display the tabs and then the subsequent ones are loaded on demand.
Routing.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { AppComponent } from 'src/app/app.component';
import { IllinoisComponent } from 'src/Illinois/IllinoisComponent';
import { NewYorkComponent } from 'src/NewYork/NewYorkComponent';
import { CaliforniaComponent } from 'src/California/CaliforniaComponent';
export const MyRoute =
[
{path: '*', component: AppComponent},
{ path: 'Illinois', loadChildren: () => import('../Illinois/IllinoisModule').then(m => m.IllinoisModule) },
{path: 'NewYork', loadChildren: () => import('../NewYork/NewYorkModule').then(m => m.NewYorkModule) },
{path: 'California', loadChildren: () => import('../California/CaliforniaModule').then(m => m.CaliforniaModule) },
]
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(MyRoute)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
Below is the code for file IllinoisModule. It imports the IllinoisRoute as Child connects it with IllinoisComponent. The imports and component declaration are done in the @NgModule decorator and can be seen in the code file below:
IllinoisModule.ts
import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { IllinoisComponent } from './IllinoisComponent'
import { IllinoisRoutes } from '../Routing/IllinoisRouting'
import { IllinoisRouteModule } from '../Routing/IllinoisRouting'
@NgModule({
declarations: [
IllinoisComponent
],
imports: [
CommonModule,
RouterModule.forChild(IllinoisRoutes),
FormsModule,
ReactiveFormsModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [IllinoisComponent]
})
export class IllinoisModule { }
The code for IllinoisRoute.ts is below. Here we are importing the IllinoisRoutes as child and creating a path to call the Illinois Component.
When the tab ‘Illinois’ is clicked, the request will go to the Routing.ts and it finds the entry of ‘Illinois’ in the collection and then the subsequent request will go to IllinoisModule which will search for the path in the IllinoisRoute.ts. In the app.component.html, the routerLink is ‘/Illinois/View’ where Illinois is the router path in Routing.ts and then ‘View’ is the subsequent path in its own Router file ‘IllinoisRoute.ts’. So we can create multiple collection using this example and route through lazy loading.
app.component.html
<a [routerLink]="['/Illinois/View']"> Illinois </a>IllinoisRoute.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { IllinoisComponent } from '../Illinois/IllinoisComponent'
export const IllinoisRoutes: Routes = [
{path: 'View', component: IllinoisComponent}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forChild(IllinoisRoutes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class IllinoisRouteModule { }
The similar code can be done for NewYork/California components as well. Please contact me to know more or the link for working project. To verify, go to Chrome’s developer tool extension and check the main.js file, it should not have the component declaration only for the component that is requested.
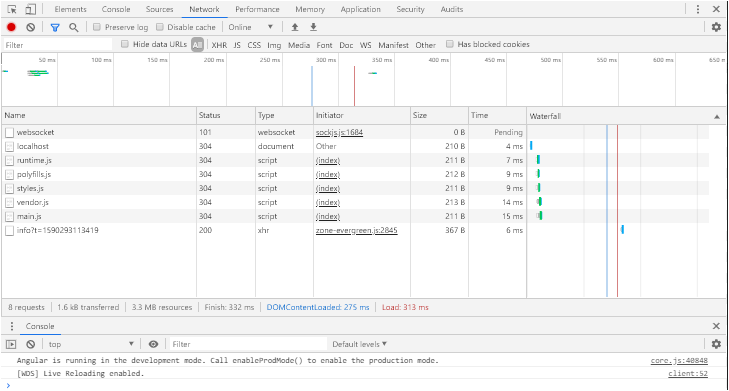
The theory in practice looks like below: