Angular Pipes
Angular piping is the process of filtering an incoming value and applying transform to change the format and display on browser using DOM.
Angular provides inbuilt pipes and custom pipes. In this tutorial, we will look at some of the inbuilt pipes and see how it looks on the UI then go on to create a sample custom pipe and see its effect on UI.
Inbuilt Pipes
There are several inbuilt pipes provided by angular. Below are the ones I am demonstrating in this tutorial:
- Uppercase pipes.
- Decimal pipes
- Date format pipe
Let’s start with the view:
app.component.html
<tr>
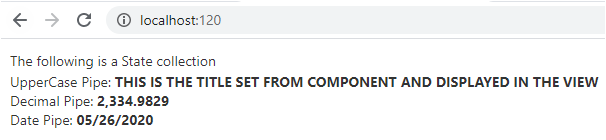
UpperCase Pipe: <b>{{ title | uppercase}}</b><br/>
Decimal Pipe: <b>{{ 2334.9829 | number: '2.3-4' }}</b><br/>
Date Pipe: <b>{{ myDate | date:'MM/dd/yyyy' }}</b>
</tr>
The format of piping in the expression {{ value | pipe }} will tell the compiler to format the value based on the pipe.
As you can see from above example, title has been formatted to Upper case. The decimal pipe will format the number based on the ‘2.3-4’ where 2 is the main integer with atleast 4 decimal places. Similarly, date pipe will format the myDate in ‘MM/dd’yyyy’ format.
UI
Now, the point in question, what if I need to format display value based on certain conditions/calculation/string operations, etc. Angular provides Custom piping through PipeTransform class. We have to create a typescript inheriting from PipeTransform and bind the pipe to the input variable.
Custom Pipes
Let’s create a ‘CalculatorPipe.ts’ in the Helpers.
Open the Calculator.ts file and write the below code.
CalculatorPipe.ts
import {Pipe, PipeTransform} from '@angular/core';
@Pipe ({
name : 'calculator'
})
export class CalculatorPipe implements PipeTransform {
transform(val0 : number, val1 : number, val2: number) : number {
return (val1 * val2 * (Math.round(val0)));
}
}
We have to inherit a class from PipeTransform provided by angular/core namespace and write the transaformation method in the transform class and return based on the specified type.
The @Pipe decorator name will be used to refer this transformation class in the consumed module.
app.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { MyRoute } from '../Routing/Routing';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { City, States, BaseClass } from 'src/Helpers/DependencyInjection';
import { CalculatorPipe } from 'src/Helpers/CalculatorPipe';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
CalculatorPipe
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
RouterModule.forRoot(MyRoute),
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
In the app.module.ts, import the CalculatorPipe and then provide them under the NgModule’s declaration to inform the Angular that we are using a custom pipe named as ‘CalculatorPipe’.
app.component.ts
<table>
<tr>
<table class="gradienttable">
<tr>
The following is a
{{loadPanel == 'States' ? 'State' : (loadPanel == 'City' ? 'City' : 'null')}}
collection
</tr>
<tr>
UpperCase Pipe: <b>{{ title | uppercase}}</b><br/>
Decimal Pipe: <b>{{ 2334.9829 | number: '2.3-4' }}</b><br/>
Date Pipe: <b>{{ myDate | date:'MM/dd/yyyy' }}</b>
Custom Multiply: <b> {{ 249.9 | calculator : 10 : 20 }}</b>
</tr>
</table>
</tr>
</table>
Now, in the app.component.html, we specify a custom pipe as below. Since we named this pipe as calculator, we will follow the same syntax as inbuilt pipe but provide the exact pipe name with parameters syntax (pipename : param1 : param2)
Custom Multiply: <b> {{ 249.9 | calculator : 10 : 20 }}</b>
Ng Serve for UI
